Affiliate/Ads disclaimer: Some links on this blog are affiliate/ads links to support this project going on, meaning I may earn a commission at no extra cost to you.

A Complete Guide to n8n AI Agents: From Beginner to Expert
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital world, repetitive tasks are silently consuming our valuable time and creativity. Manual data processing, customer service responses, and information analysis—these seemingly “small” tasks can cumulatively leave us exhausted and unproductive.
Fortunately, we no longer need to handle everything manually. With n8n, a powerful, fair-code licensed workflow automation tool, combined with large language models (LLMs), you can build AI-powered digital employees that work 24/7, automatically handling everything from data collection and cleansing to analysis and decision execution.
Core Philosophy: You don’t need to write all the code yourself, but you must know how to design workflows.
What are n8n and AI agents?
n8n (pronounced “n-eight-n”) is a node-based low-code/no-code automation platform that allows you to connect different services (like email, databases, APIs, and AI models) through a graphical interface, forming complete workflows.
An AI agent builds upon large language models (LLMs), which generate text by predicting the next word based on input. While LLMs only process input to produce output, AI agents add goal-oriented functionality. They can use tools, process their output, and make decisions to complete tasks and solve problems.
In n8n, AI agents appear as nodes with additional connections, enabling you to combine AI-driven steps with traditional programming for efficient, real-world workflows.
Key Differences: LLM vs. AI Agent
The table below illustrates the core differences between basic LLMs and AI agents:
flowchart TD
subgraph A [Large Language Model]
direction LR
A1[Input] --> A2[LLM]
A2 --> A3[Text Generation]
end
subgraph B [AI Agent]
direction LR
B1[Goal] --> B2[AI Agent]
B2 --> B3[Tool Usage]
B3 --> B4[Decision Making]
B4 --> B5[Task Completion]
end
A --> B
linkStyle default stroke:#fb923c,stroke-width:4px;| Feature | LLM | AI Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Core Capability | Text generation | Goal-oriented task completion |
| Decision-Making | None | Yes |
| Tool/API Usage | No | Yes |
| Workflow Complexity | Single-step | Multi-step |
| Scope | Generate language | Execute complex real-world tasks |
| Example | LLM generates a piece of text | An agent that schedules appointments |
Why n8n AI Agents? Real-World Applications
Future work patterns are shifting from being “executors” to becoming “commanders.”
Practical Application Scenarios
Customer Service Automation
- Users ask questions in chat windows
- Workflow automatically queries databases → Calls AI for summarization → It returns structured recommendations.
Job Search Assistant
- Daily scans of job platforms for specific positions
- Automatic filtering of “starred companies” + “matching skill stack” jobs
- AI-generated personalized resumes → Automatic submission → SMS notifications
E-commerce Price Monitoring
- Scheduled scraping of identical products across platforms
- Data cleansing and alignment → Calculate lowest prices → Email “Today’s Best Discounts.”
Key Insight: Any task that is rule-based, repetitive, and high-frequency deserves to be automated!
Getting Started: Environment Setup
Method 1: npm Installation (Suitable for Developers)
# Check Node.js version (requires v16+)
node -v
# Install n8n globally
npm install -g n8n
# Start service
npx n8nVisit http://localhost:5678 to get started.
Method 2: Docker Installation (Recommended—Zero Dependencies)
# Create persistent volume (prevents workflow loss)
docker volume create n8n_data
# Start container (with data persistence)
docker run -it --name n8n \
-p 5678:5678 \
-v n8n_data:/home/node/.n8n \
n8nio/n8nAdvantage: Cross-platform, no configuration required, one-click rollback.
Building Your First AI Agent: Step-by-Step Tutorial
To get your first AI agent into an application, follow these steps:
graph TD
A[Create New Workflow] --> B[Add Chat Trigger Node]
B --> C[Add AI Agent Node]
C --> D[Configure AI Agent: Add Chat Model and Credentials]
D --> E[Test Workflow]
E --> F[Save Workflow]
linkStyle default stroke:#fb923c,stroke-width:2px; Step 1: Create a New Workflow
- Select “Home” “+” to create an empty workflow.
Step 2: Add a Trigger Node
Every workflow needs a starting point.
- Press
++Tab++or click “Add first step” to open the node menu - Search for “Chat Trigger.”
- Select “Chat Trigger” to add it to the canvas
Step 3: Add AI Agent Node
The AI Agent node is core to adding AI to your workflow.
- Click the “Add node” connector on the trigger node
- Type “AI” and select “AI Agent” node to add it
Step 4: Configure the Node and Add Credentials
The AI agent needs to connect to a chat model to process incoming prompts.
- Click the “+” button under the “Chat Model” connection in the AI Agent node
- Select “OpenAI Chat Model” from the list
- Add credentials (API key) for OpenAI or your preferred model provider
Step 5: Test and Save
- Click the “Chat” button at the bottom of the canvas
- Type a message and press
++Enter++ - Observe the AI response in the chat interface
- Save your workflow to preserve all changes
Advanced AI Agent Configuration
Adding Persistent Memory
By default, AI Agents don’t retain context between messages. To create conversational agents that remember previous interactions, you need to add memory:
- Add a “Memory Store” node to your workflow
- Connect it to the AI Agent’s memory connection
- Configure what conversation context to retain
- Set up memory pruning rules to manage storage size
Multi-Agent Collaboration
For complex tasks, you can create specialized agent teams:
flowchart LR
A[User Input] --> B[Orchestrator Agent]
B --> C[Research<br>Specialist]
B --> D[Analysis<br>Specialist]
B --> E[Content<br>Creator]
C --> F[Memory Store]
D --> F
E --> F
F --> G[Final Response]
linkStyle default stroke:#fb923c,stroke-width:4px; This multi-agent approach allows for specialized task handling while maintaining cohesive output.
Tool Integration
AI agents in n8n can utilize various tools through node connections:
- HTTP Request Node: API calls to external services
- Code Node: Custom JavaScript/Python for specialized processing
- Database Nodes: Direct data querying and manipulation
- File Processing Nodes: Handle documents, images, and structured data
Practical Example: Building an Intelligent Customer Service Agent
Let’s create a comprehensive customer service agent that:
- Understands Customer Queries (Chat Trigger + AI Agent)
- Searches Knowledge Base (HTTP Request/Code Node)
- Provides Contextual Responses (AI Processing)
- Escalates Complex Issues (If Node + Email Node)
- Learns from Interactions (Memory Store + Database)
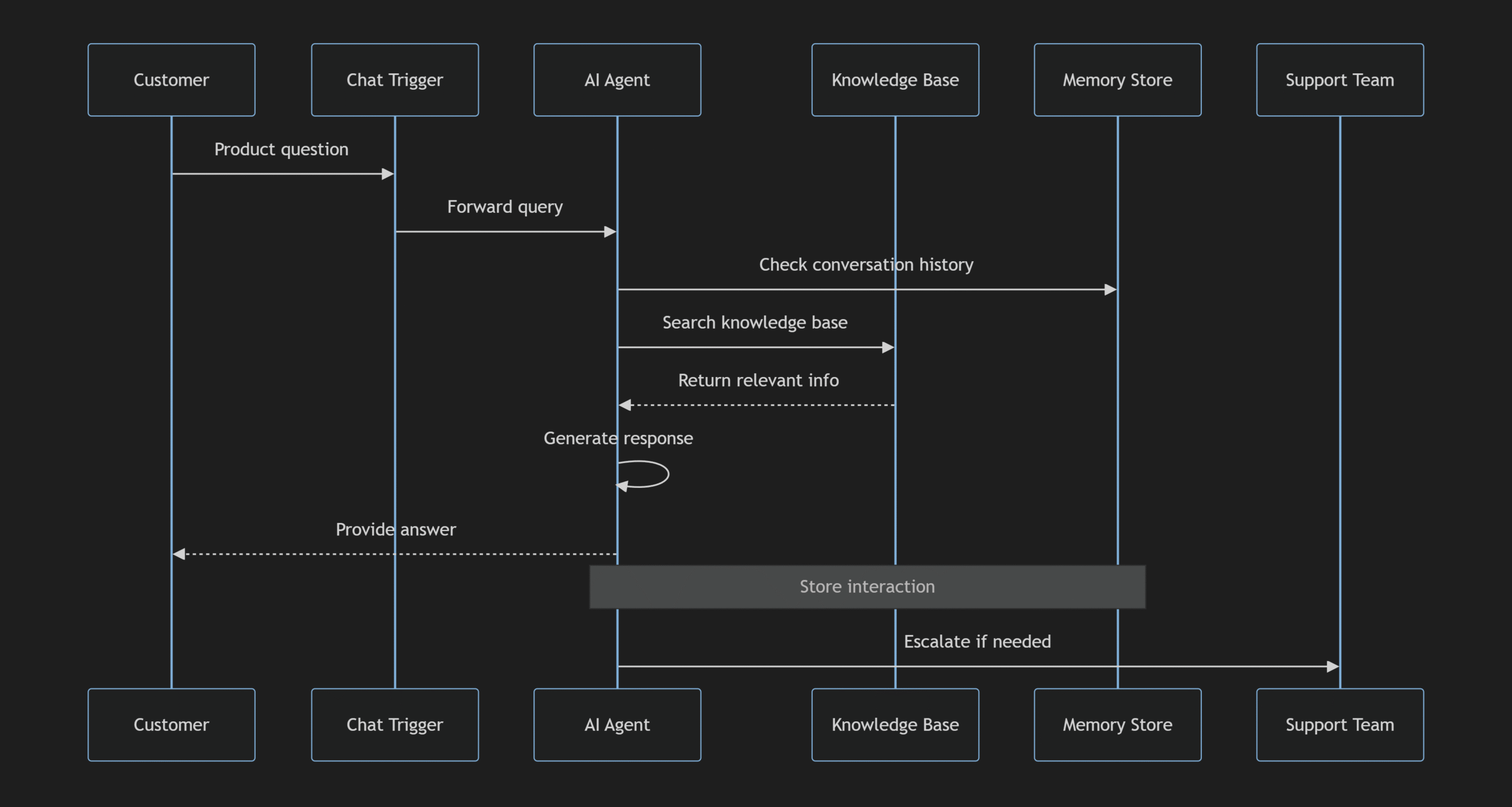
Workflow Architecture:
sequenceDiagram
participant C as Customer
participant T as Chat Trigger
participant A as AI Agent
participant K as Knowledge Base
participant M as Memory Store
participant S as Support Team
C->>T: Product question
T->>A: Forward query
A->>M: Check conversation history
A->>K: Search knowledge base
K-->>A: Return relevant info
A->>A: Generate response
A-->>C: Provide answer
Note over A,M: Store interaction
A->>S: Escalate if needed The above is using Mermaid text to sequenceDiagram to demonstrate full process. Here is the image version for your download and saved:
Best Practices and Pro Tips

1. Effective Prompt Design
- System Prompts: Clearly define the AI’s role and capabilities
- Context Management: Balance sufficient context with token limits
- Output Formatting: Specify exact response formats for consistent parsing
2. Error Handling and Validation
- Implement fallback mechanisms for AI failures
- Add input validation nodes before AI processing
- Create retry logic for external API calls
3. Performance Optimization
- Cache frequent AI responses where appropriate
- Use parallel processing for independent tasks
- Implement request batching to reduce API calls
4. Security Considerations
- Secure credential management using n8n’s credential system
- Input sanitization to prevent prompt injection
- Output filtering for sensitive information
Common Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| AI Hallucinations | Add fact-checking nodes and verification steps |
| Context Limitations | Implement summarization for long conversations |
| API Rate Limits | Add rate limiting and queueing mechanisms |
| Cost Management | Cache responses and monitor usage metrics |
| Response Consistency | Use strict output schemas and validation |
Resources and Next Steps
Learning Resources
- n8n Official Docs: https://docs.n8n.io/
- n8n Chinese Tutorial Community: https://n8n.akashio.com/
- n8n Workflow Templates: https://n8nresources.dev/ (5,628+ free templates)
- GitHub n8n-workflows: https://github.com/Zie619/n8n-workflows (2,053 workflow templates)
Template Collections
- n8n Official Template Library: 1500+ community templates
- n8n Resources: 5,628+ curated workflows across 400+ integrations
- n8n-workflows GitHub: 2,053 professionally organized workflows with documentation system
Conclusion: Becoming an AI Workflow Designer
n8n is not just a tool; it embodies an automation mindset. It liberates us from tedious operations, allowing focus on higher-value creative work.
Remember: In the future, those who cannot design AI workflows might be replaced by those who can.
Just as Excel transformed financial work, n8n is reshaping how development, operations, product, marketing, and various other roles work. Every workflow is an AI agent—it can understand instructions, acquire information, make judgments, and execute actions.
Now, open http://localhost:5678 and create your first automated workflow! Let AI become your most capable digital employee.






